Automating Kubernetes Deployments with Argo CD Image Updater
Modern DevOps teams strive for speed, reliability, and automation in their deployment pipelines.
In Kubernetes environments, Argo CD is the de-facto GitOps controller — but manually updating image tags in manifests can quickly become a bottleneck.
This post explains how to eliminate that manual step using Argo CD Image Updater, ensuring your deployments stay aligned with the latest container images automatically.
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
- 💡 The Problem — Manual Tag Updates
- Architecture Overview
- Prerequisites
- Step 1: Install Argo CD
- Step 2: Create a Sample Application
- Step 3: Register the Application
- Step 4: Install Image Updater
- Step 5: Configure Image Update Strategy
- Step 6: Configure Git Credentials
- Step 7: Test Auto-Update
- Step 8: (Optional) Enable PR Mode for Safer Updates
- Verification
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- References
💡 The Problem — Manual Tag Updates
Here’s what happens in a traditional CI/CD setup:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub or GitLab.
- A CI pipeline (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) builds a Docker image with a new tag.
- The new image is pushed to your registry (Docker Hub, Nexus, Harbor, etc.).
- The CD pipeline updates Kubernetes manifests (via shell script or manual commit).
- Argo CD detects the change and syncs your cluster.
Drawback
Your CD pipeline depends on the CI pipeline.
If your CI job fails to update the manifest (for example, due to Git credentials or token issues), the CD step never triggers — even if a new image is already available in the registry.
That’s where Argo CD Image Updater comes in.
Argo CD Image Updater is an official Argo CD add-on that:
- Watches container registries for new image tags.
- Automatically updates image tags in your GitOps repository.
- Optionally creates pull requests for human review (PR mode).
- Triggers Argo CD to sync the changes into your Kubernetes cluster.
This effectively decouples CI from CD — meaning your cluster updates automatically when a new image is available, even if the CI pipeline is idle.
Architecture Overview
Here’s the updated GitOps flow with Argo CD Image Updater:
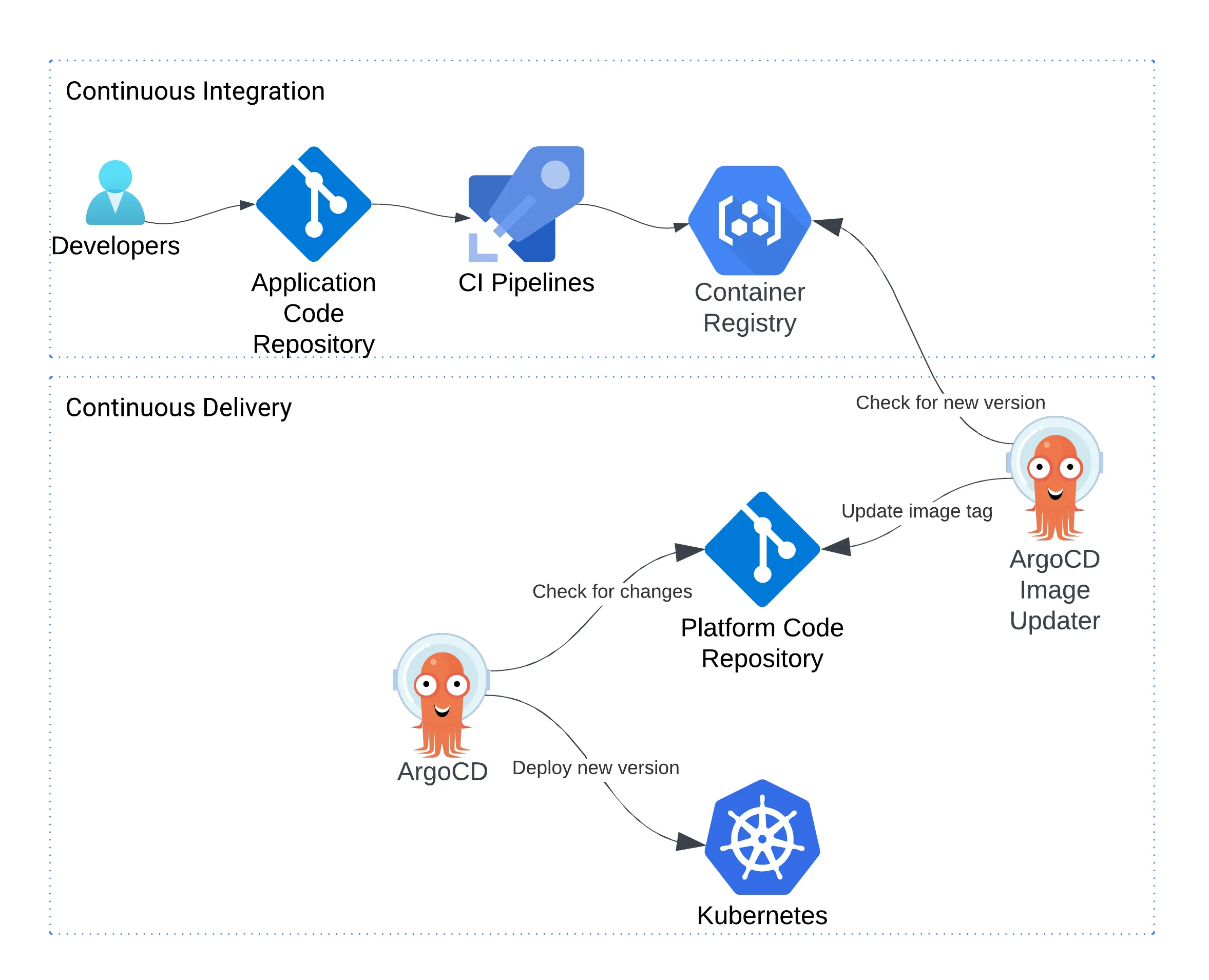
Workflow Summary:
- CI pushes a new image tag.
- Argo CD Image Updater detects it.
- It commits the updated manifest to Git.
- Argo CD syncs and deploys the new version automatically.
Git remains the single source of truth.
Deployments are traceable and reproducible.
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have:
- A Kubernetes cluster (e.g., Minikube, EKS, GKE, or AKS)
- Argo CD installed and running in the
argocdnamespace - kubectl installed and configured
- A Git repository containing your Kubernetes manifests
- Optional: Docker registry credentials (for private images)
Step 1: Install Argo CD
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Expose Argo CD server (NodePort)
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
Retrieve admin password:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
Access the UI via:
https://<minikube-ip>:31154
Step 2: Create a Sample Application
Deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-web-app
labels:
app: my-web-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-web-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-web-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-web-app
image: abhizeet/sample-flask-app:v1.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-web-app
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: my-web-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
kustomization.yaml
resources:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
Commit and push to your Git repository.
Step 3: Register the Application
In Argo CD UI:
- Application Name:
webapp - Project: default
- Repository URL: your Git repo URL
- Path:
. - Cluster: your Kubernetes cluster
- Namespace: default
- Sync Policy: automatic
Click Create → Argo CD will deploy your application.
Step 4: Install Image Updater
Install Image Updater in the same namespace as Argo CD:
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj-labs/argocd-image-updater/master/manifests/install.yaml
Check that the pod is running:
kubectl get pods -n argocd | grep image-updater

Step 5: Configure Image Update Strategy
Argo CD Image Updater uses annotations on your Argo CD Application to determine:
-
Which image to track
-
Which update strategy to use
-
What to do when an update is found
Example (semantic versioning):
Edit your Argo CD Application annotations:
kubectl edit app webapp -n argocd
Add these annotations:
metadata:
annotations:
argocd-image-updater.argoproj.io/image-list: abhizeet/sample-flask-app:v1.x
argocd-image-updater.argoproj.io/sample-flask-app.update-strategy: semver
argocd-image-updater.argoproj.io/write-back-method: git:secret:argocd/git-credentials
This means:
-
Track image sample-flask-app
-
Update using semantic versioning (e.g., v1.2.3)
-
Write changes back to Git when a new version is found
Step 6: Configure Git Credentials
The Image Updater needs write access to your Git repo to commit updated manifests.
Option 1: HTTPS (Personal Access Token)
Create a secret:
kubectl create secret generic git-credentials \
-n argocd \
--from-literal=username=<git-username> \
--from-literal=password=<git-token>
Then, in the annotation as already mentioned in step 5:
argocd-image-updater.argoproj.io/git-credentials=secret:argocd/git-credentials
Option 2: SSH (Recommended)
Generate key:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "argocd@yourcompany" -f /etc/argocd/keys/argocd-key
Add the public key as a Deploy Key in GitHub and use the private key to register the repo in Argo CD:
argocd repo add git@github.com:<username>/<repo>.git \
--ssh-private-key-path /etc/argocd/keys/argocd-key
Step 7: Test Auto-Update
Push a new Docker image tag:
docker tag my-web-app:v1.2 my-web-app:v1.3
docker push my-web-app:v1.3
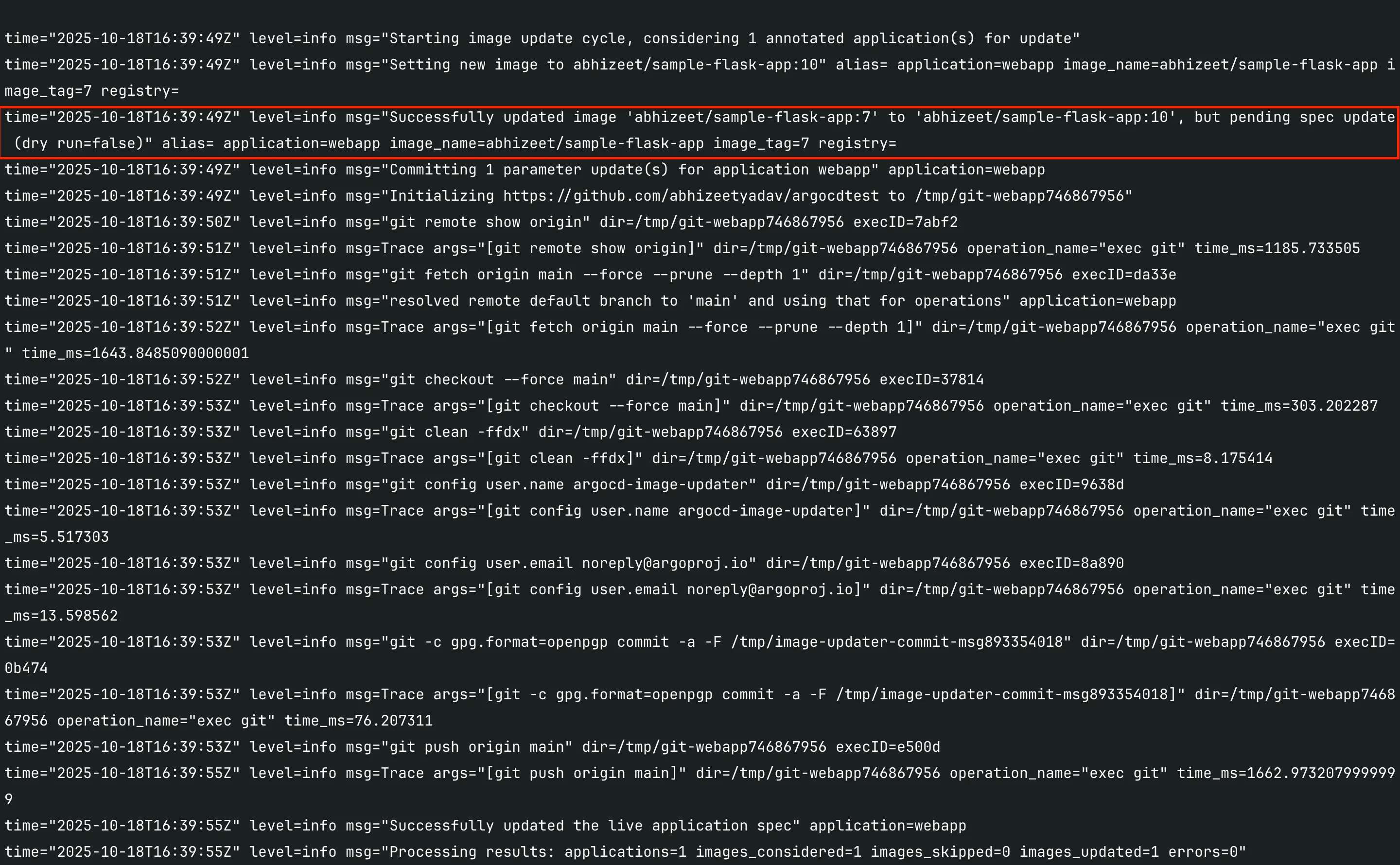
Check Image Updater logs:
kubectl logs -n argocd deploy/argocd-image-updater -f
Expected Log Snippet
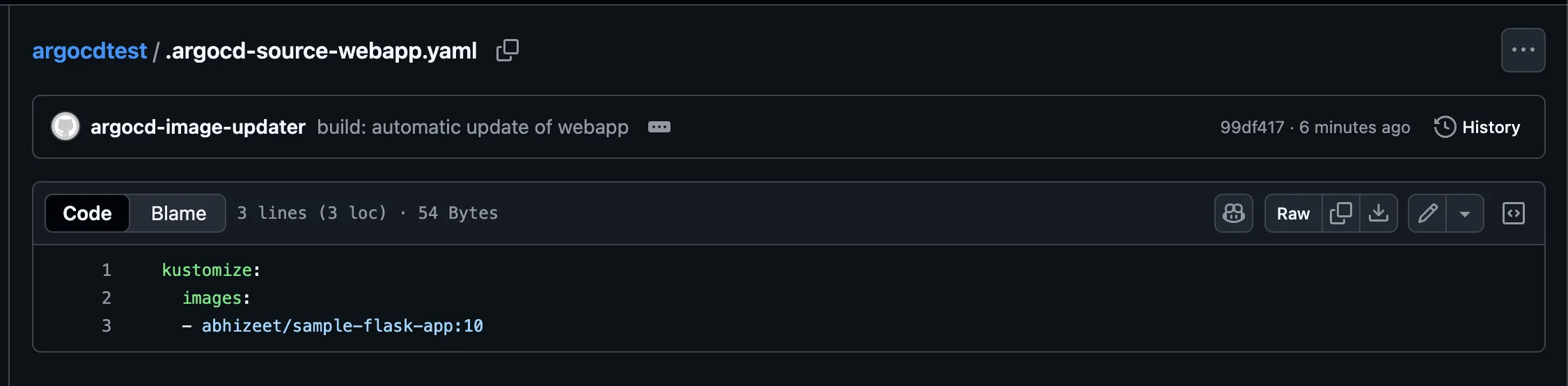
Refresh your Git repo — the Deployment.yaml or kustomization.yaml should now reference new version.
Argo CD detects the manifest change and auto-syncs the cluster.
Step 8: (Optional) Enable PR Mode for Safer Updates
Instead of directly committing to the main branch, let Image Updater create a Pull Request.
Edit the ConfigMap:
kubectl edit configmap argocd-image-updater-config -n argocd
Add:
git.write-back-method: "pull-request"
git.user: "argocd-bot"
git.email: "argocd-bot@yourcompany.com"
Now, every new image tag will generate a PR you can review and merge manually.
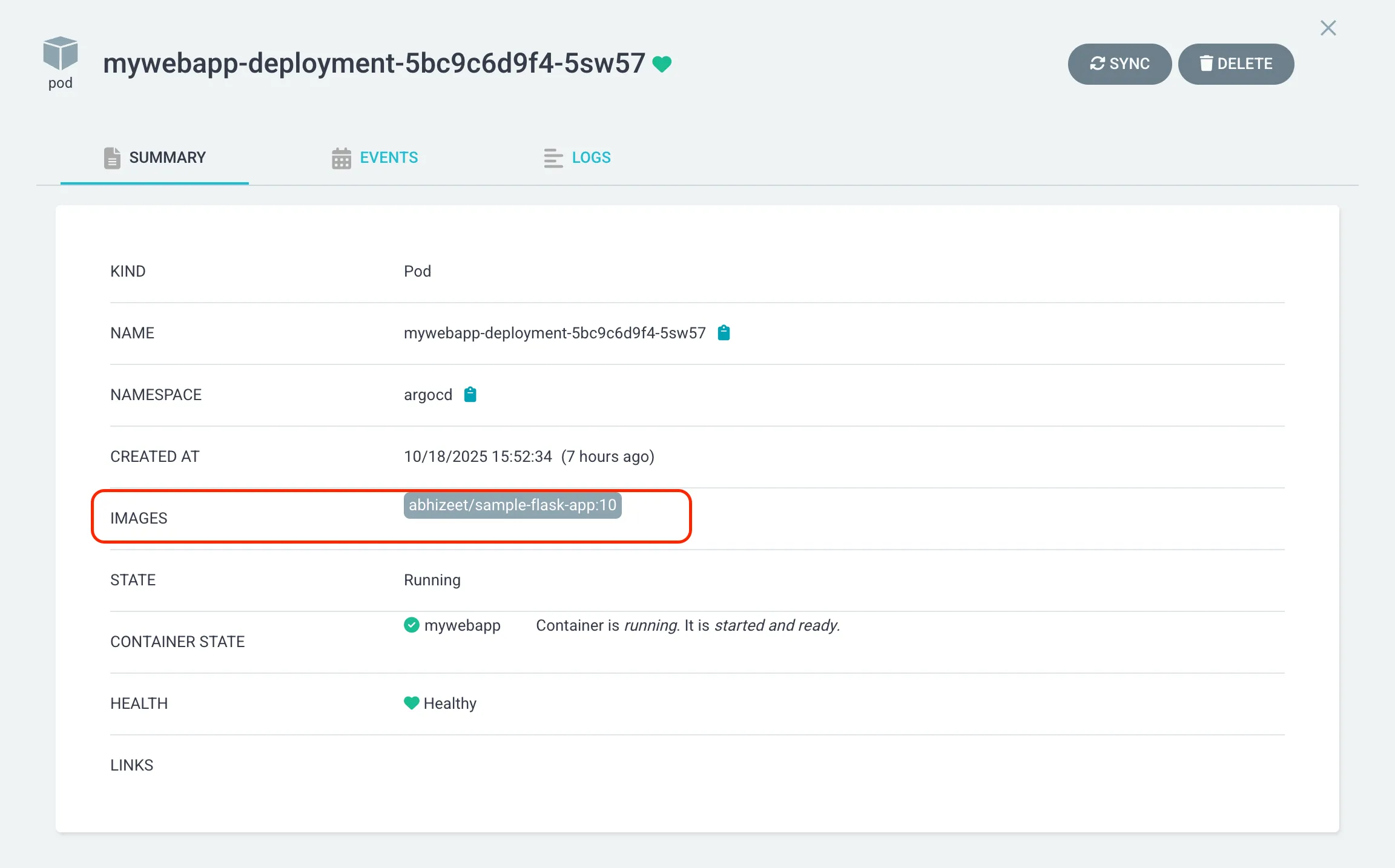
Verification
Check Argo CD UI — you should see the new image tag automatically reflected and synced.
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Repository not accessible | Invalid Git credentials | Verify token or SSH key |
| ImagePullBackOff | Registry authentication issue | Add imagePullSecret to deployment |
| Updater not committing | Insufficient Git write access | Check token permissions (repo:write) |
| Stuck in OutOfSync | Argo CD sync disabled | Enable auto-sync |
Conclusion
With Argo CD Image Updater, your Kubernetes deployments become truly self-updating and GitOps-compliant.
By automating image tag updates and syncing directly through Git, you ensure your environments remain consistent, auditable, and production-ready.
Automation. Stability. GitOps. — that’s the Argo way.